Overview of Eczema
‘Eczema’ is a very commonly known skin condition. It is a Greek word. The meaning of eczema is ‘to boil’. Many people use the word eczema to refer to atopic dermatitis. But in actual the term atopic is a collection of different conditions involving your immune system. Hay fever, Asthma, Atopic dermatitis all are included under this name.
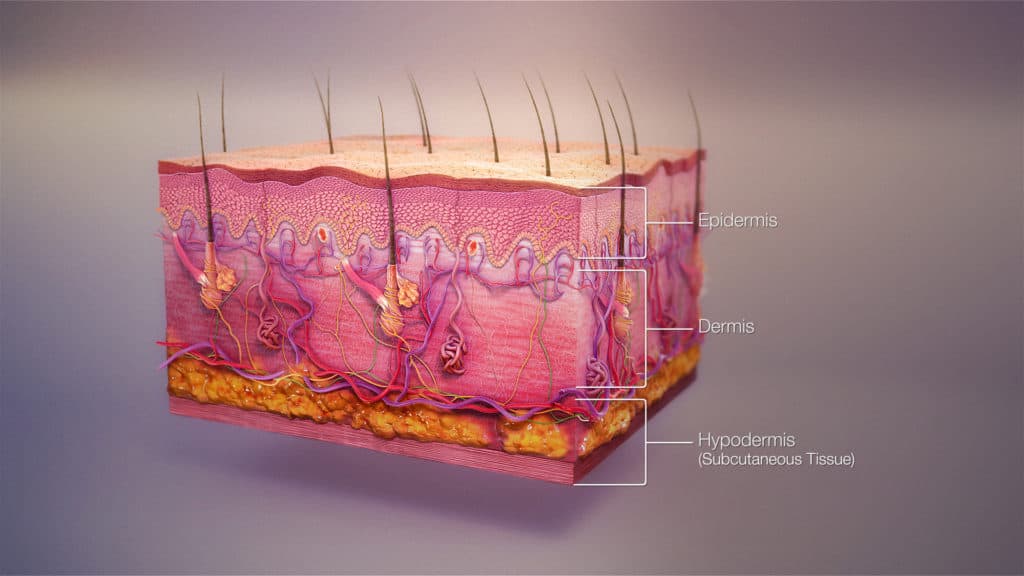
- Human body skin is made up of two primary layers – the dermis and epidermis.
- The epidermis layer consists of keratinocytes, melanocytes, Merkle cells, and Langerhans cells. This layer acts as a barrier to infection. It regulates body temperature. It has no blood vessel of its own. So, it is nourished by diffusion. Waterproofing is also done by this layer.
- The dermis layer is comprised of hair follicles, connective tissues, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels.
- There is a sub-layer named hypodermis. It lies underneath the skin. It connects the skin with the underlying bones and muscles.
- Eczema occurs in the epidermis layer. It is a reaction pattern due to inflammation of the epidermis. If there is any damage occurs in this layer; as a result, eczema occurs. Common manifestations of Eczema are crusting and scaling of the skin. Usually, these types of skin lesions start with itching then rashes appear.
- Eczema makes the epidermis layer drier. Besides erythema (redness), flakes, blisters, crack, infection is also a common phenomenon in this disease.
Epidemiology of Eczema
- About 31.6 million people in the United States are affected by different stages and types of eczema, which is almost over ten percent of the population.
- The worldwide prevalence of atopic dermatitis is 0.9% in adults and ten to twelve percent in children. It has a higher prevalence among Asians and blacks.
- Babies and toddlers are common sufferers of this. Though adults may also be equally affected by this.
Causes of Eczema
- The etiology of eczema is widespread. It includes autoimmune, idiopathic, inflammatory, allergic mechanisms. People with eczema are unable to retain moisture in their skin, as a result, it becomes drier. So, it can easily be triggered by many factors and cause soreness and intense itching.
- You may be born with an increased tendency to develop atopic eczema, because your parents may carry the genes responsible for atopic eczema. Studies suggest people who develop atopic eczema may have other siblings or one of the parents or both parents affected with it.
- Atopic eczema is not contagious so you cannot pass it through close contact.
- There is a common etiologic hypothesis regarding Eczema. It suggests immune dysfunction leading to defective epithelial cells and immunoglobulin (IgE) sensitization. These factors disrupt the skin’s epithelial barrier.
Symptoms of eczema
People with eczema develop a rash which can be:
- Itchy
- Red
- Dry
- Scaly
- Cracked
- Sore
- Formation of small blisters
It is seen that Eczema symptoms worsen at night. The reasons are:
- Most people tend to scratch during sleeping. It makes itching worse. Most of them are sleepy so they forget that itching will make their condition worse.
- Our body’s wake and sleep cycles. Human body temperature decreases at night. It makes our skin feel itchier.
- If you put moisturizer during the daytime, its effect diminishes during nighttime. As a result, your skin will become dry and symptoms will get more prominent.
Types of eczema and their varieties of symptoms
Atopic eczema
It is widely known as atopic dermatitis. One of the very common forms of eczema is atopic eczema. It is a pruritic disease. It is also known as atopic dermatitis. The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not known. Typically, it starts in infancy. But adults are also affected by this condition. In this condition, the skin becomes dry, itchy, sore, and cracked. Any part of the body can be affected by Atopic eczema. But very frequently it affects the hands, neck, face, elbows (mostly inner side), back of knees, torso (trunk), top of the feet, front of the knees. But in the case of adolescents, the usual site for atopic eczema is their scalp. Some of you may have small patches of dry skin. Some may have widespread inflamed skin in their body. Sometimes atopic dermatitis is associated with other atopic disorders such as asthma, urticaria, allergic rhinitis.
Seborrheic dermatitis
It happens in areas of your body having lots of oil glands. In this type of eczema scaly, red patches evolve on the sides of the ears, eyebrows, nose, and scalp. Patches appear mostly in the scalp as then it is known as dandruff. Scalp lesions in the toddler appear greasy and yellowish. It is said as cradle crap. It doesn’t cause any discomfort to them. A yeast named Malassezia furfur is usually the causative agent of it.

Varicose Eczema
In this type of eczema mostly affects the lower part of the leg. If there is any problem in the flow of blood through the leg veins then it develops. It is also known as gravitational eczema or stasis eczema.

Allergic Contact dermatitis
It is a delayed-type IV hypersensitivity reaction in which antigens are carried by Langerhans cells to regional lymph nodes, then they are presented to T lymphocytes and it reproduces more lymphocytes. It may take ten to fourteen days. It occurs when the body comes into contact with a particular substance that is allergic to the affected person. Symptoms can range from mild redness to severe skin blistering. It can also lead to ulceration. When your skin is triggered by any kind of allergic reaction, it makes your skin red, it may form blisters or fine bumps. Severe itching is also a very important characteristic.
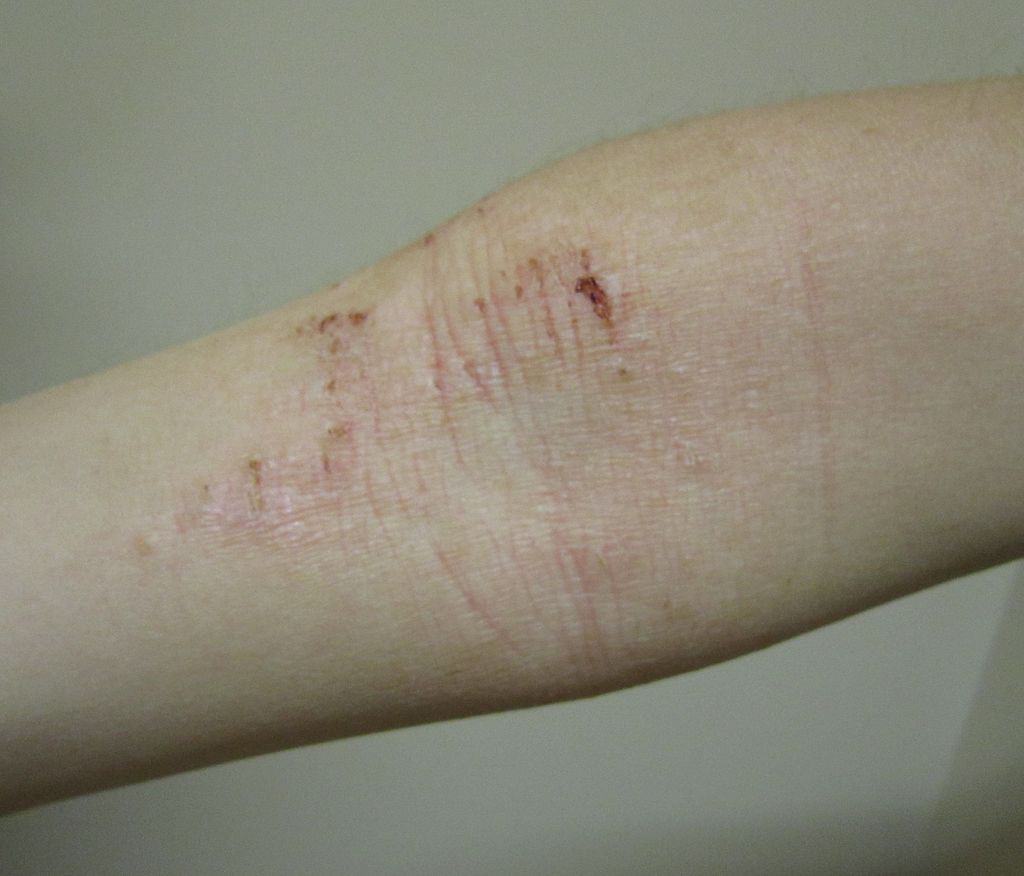
Irritant contact dermatitis
when human skin comes in contact with any sort of irritant substance, then this type of eczema develops. It is widely known as irritant contact dermatitis. redness (in mild form) to severe skin blistering or even ulceration can occur. Usually, a person having plant allergies such as poison oak or poison ivy can vet this type of eczema. It is very intense and harmful also. Initially, it starts with bumps and blisters in line. You may develop streaks when the skin comes in contact with the plant.

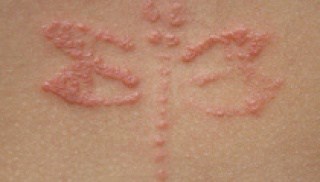
Discoid Eczema
It is also known as Nummular Eczema. In this variety oval-shaped patches or circular patches develop in the skin.
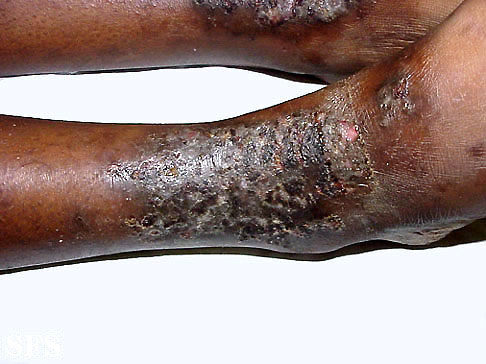
Dyshidrotic Eczema
Another name of this is pompholyx. It is a chronic relapsing form of vesicular palmoplantar dermatitis. Etiology is still not known. It is a fact that fifty percent of this patient concurrently also develops atopic dermatitis. Some exogenous sources may play a triggering factor such as nickel or some kind of metal. This variety of eczema, an eruption of tiny blisters occurs across the palm of the patient. On clinical examination, symmetric crops of clear vesicles were found on the palm, toes, and lateral fingers and soles. Vesicles formed in this eczema are deep-seated and usually surrounded by erythema. It may be confluent to form bullae which may rupture easily. The lesion mostly (eighty percent) distributed in hands, ten percent in feet, and ten percent in hands. Diagnosis is mostly clinical but to confirm this punch biopsy is required. Patients with mild symptoms resolve within three weeks. Bullae are drained without unroofing of the skin or sometimes may be treated with burrow’s solution compresses. Some therapies include topical or systemic corticosteroids, ultraviolet-A therapy, topical calcineurin therapies.

Asteatotic Eczema
It is also known as xerotic eczema, it develops as a result of dry skin. It is a common type of dermatitis. A common site of asteatotic eczema is your lower legs. It causes stingy pain in areas of cracked, dry, and reddened skin. It causes itching in the affected areas.
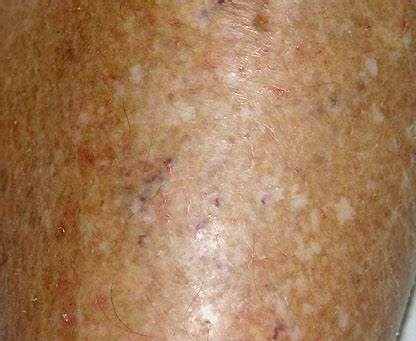
Hand eczema
It generally appears as patches of cracked, dry skin during the winter season. It may cause itching. Sometimes blisters, scaling red bumps may also occur. Redness may or may not occur. When washing with soap, the soapy water may trap under rings and it irritates the hand.

Stasis eczema
This type of eczema occurs in people having poorly functioning veins on the lower legs. The usual site of stasis dermatitis is legs, ankles, calves, feet which are already swollen and puffy. Initially, it starts with itching and a mild redness of the lower legs or maybe darkening of skin tone. Weeping sores are also common signs. If all of a sudden it turns tender and becomes redder; then there is a possibility of secondary bacterial infection. It requires urgent medical attention.
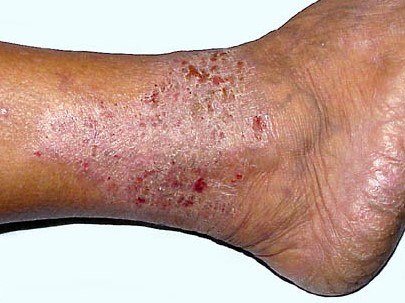
Lichen simplex chronicus
It is also known as neurodermatitis, in this type of eczema, the rash becomes thickened. It will turn your skin leathery with a darkening of color. It is very itchy. Frequent itching makes the condition worse. Autoimmune progesterone dermatitis may flare up in women during the menstrual cycle. Though it is a very rare condition. You must avoid medicine containing progesterone then.

Triggering factors of Eczema
It may vary from person to person. Various triggering factors can worsen your eczema symptoms. Such common triggering points are given below:
- Environmental factors – Extreme weather such as dry or cold weather put a negative impact on the person’s skin. Apart from these, having a pet can also add to this list as some people’s skin is sensitive to pet fur. Besides damp weather, dust mites, molds, pollen also can trigger eczema.
- Hormonal changes – Especially women going through hormonal changes before menstruation/period; their eczema symptoms may flare-up. Some women during pregnancy also face the same situation.
- Allergens or irritants – Some of us may be affected by some sorts of detergents, soaps, shampoos, even dishwashing liquids or bubble baths.
Some chemicals, fabrics, metal may add to this list.
- Food allergies – Some foods may cause allergies such as- nut (peanut; walnut or almonds), soy products, eggs, wheat, shellfish, cow milk, seafood.
- Airborne allergens – such as mold, dust, smoke, pollen aggravate eczema.
- Keeping pets – their fur or feather, untidy house, using dusty carpets, using air conditioner, smoke all these things act as triggering factors.
- Sweat may worsen eczema. So, use comfortable clothes and avoid heavy exercise to improve your condition.
Eczema Diagnosis
Diagnosis of eczema is mostly clinical. Depending on your skin symptoms and patterns of skin problems doctor may ask few questions –
- History of exposure to any kind of irritant chemical or materials.
- Any kind of personal allergy.
- If your family has any allergy history.
- Close contact with any factor which can trigger your symptoms- any plants, insects, poison ivy, etc.
- By examining your skin.
- By doing a skin patch test.
Differential diagnosis
The following diseases may mimic some signs of eczema –
- Lichen planus – it is itchy and can be leathery like eczema. But, the purplish color, white lacy patches over the lesions differentiates it from eczema.
- Plaque psoriasis – it can be itchy but the presence of thick silvery scales and Auspitz sign can differentiate it from eczema.
- Actinic keratosis – may look similar to seborrheic dermatitis especially if present on the scalp. But absence of dandruff and presence of burning sensation can differentiate it from seborrheic dermatitis.
Eczema reatment
Home remedies
People with eczema may try some useful home remedies which can improve their symptoms and maintain their skin health.
- Avoid taking baths for a longer period.
- Use moisturizer.
- Use doctor-prescribed emollients, ointment just after taking shower.
Some useful suggestions to prevent nighttime eczema scratching
The best way to prevent eczema flare is to avoid your triggering factors that may aggravate itching:
- Taking bath at night: Regularly taking shower is useful for eczema patients. It helps to keep your skin hydrated and prevent further infection. You may also try to bathe using vinegar, colloidal oatmeal.
- Use moisturizer before bed: To lock your moisture you should try to put moisturizer within three minutes after taking shower. Some oil-based moisturizers or medicated steroid creams can be helpful. But you must consult a registered doctor before using this thing. As steroids have many side effects.
- Before you sleep, avoid any type of allergens: Some people having eczema may have some allergies such as pollen flakes of pet skin, specific food he or she may be allergic to. It may worsen their symptoms. So, you should try to avoid it.
- Avoid any type of harsh fabric: If any fabric irritates your skin, you must avoid it. Some people’s skin is allergic to wool, polyester type of material. Cotton-made fabrics are gentler to your skin.
- Using a wet wrap during sleep: If your skin becomes very dry during the night, you can try wrapping a wet cloth in your eczema-affected skin. Keeping your skin wrapped overnight can keep your skin hydrated and less itchy.
- Taking over the counter medication such as antihistamines: well, taking an antihistamine will not reduce your itching; but it will make a person feeling drowsy – so he or she may fall asleep very easily and prevent herself from further itching
Signs you should contact a doctor immediately
If your skin develops severe redness/ blisters, swollen and extreme itchiness. Also, if your skin becomes extremely dry and cracked up and painful. If any pus-like discharge or streak formation happens then you must see a doctor.
Medical treatment
Doctors prescribed a variety of medications to treat the symptoms of eczema. Some of the options are given below:
- Ointments and topical corticosteroids: To relieve eczema symptoms such as itchiness and inflammation a range of corticosteroid creams and ointments are used. These are anti-inflammatory medications. Usually, these topical steroids are mild to moderate strength. When topical corticosteroids are used for a longer period to control atopic dermatitis, sometimes it is not sufficient – then your doctors may prescribe a topical calcineurin inhibitor. Children older than two years of age are sometimes suggested with tacrolimus and pimecrolimus. Again, all this medication must be used under a registered doctor’s prescription.
- Using over-the-counter oral histamines and strong steroid: Sometimes doctors prescribed over-the-counter antihistamines to treat Allergy contact dermatitis. Antihistamines can relieve the itching with Atopic eczema. They can be sedating and cause drowsiness or non-sedating. If the itching gets severe the doctor may suggest sedating antihistamine, in this case, close one of the patients should be alert that drowsiness doesn’t harm themselves.
- Doctors may also prescribe oral steroids for a short duration (five to seven days ) to control eczema flare-ups. In severe cases, specialists may use immunosuppressants. But it has some serious side effects. So before using it both physician and patient should be extremely cautious.
-
Using wet wraps and bandages: Some doctors prescribe clothing or wet wraps to put over the areas of eczema-affected skin. The use of Medicated bandages is also encouraged by some physicians.
eczema. Besides, too much exposure to UV is harmful to the skin. So before going for this type of treatment, one must talk to a qualified registered doctor and weights both its risks and benefits. Besides, doctors will closely monitor the skin.
Use of phototherapy: Some people having eczema may benefit from phototherapy. UV light affects the immune system. It can improve moderate to severe cases of eczema; whether it is from contact dermatitis or atopic dermatitis both eczema can be treated with it. Phototherapy treatment uses UV A & Blight on eczema patients. UV treatment combined with psoralen is collectively termed PUVA. But not everyone will benefit from this therapy, it may worsen some people’s
Use of antibiotics: If your skin oozes fluid or little yellowish-white spots appear in your skin, it becomes sore and there is a crust formed on the skin surface there is a higher possibility your eczema has got infected with bacteria. In this matter, your consultant will suggest antibiotics to control your skin infections.
-
Use of antiviral drugs: If your eczema gets infected with the herpes simplex virus then you need to consult a doctor urgently. It may cause you painful sores, fluid-filled blisters, feeling of unwellness. This condition is called eczema herpeticum. In this case, you need antiviral medicine such as acyclovir but make sure you discuss it with your doctor.
-
Using antifungal treatment: Adults with seborrheic dermatitis are treated with dandruff shampoo. So far it is the best treatment for them. Seldomly doctors prescribe antifungal rinses or facial creams if it is not controlled by anti-dandruff shampoo.
-
Using wet wraps and bandages: These bandages can be used over topical corticosteroids or over emollients to help the underneath skin to heal and stop drying out. It may further prevent them from scratching their skin.
Side effects of topical corticosteroids
- It may cause a mild stinging sensation for 1 to 2 minutes when you apply them to your skin.
- Changes in skin color- if you use stronger steroids for a few months your skin color will lighten. So you must consult with your doctor about this.
- Thinning of the skin- if you apply it in the wrong place such as your face or other unaffected areas for several weeks then it may happen.
- Increase hair growth in unusual areas of your skin.
- Formation of acne especially in the case of teenagers.
The risk of side effects may increase if you use strong topical corticosteroids in larger amounts, for a longer period, in sensit6 areas of skin such as the groin, armpit, face. Using this medication without consulting a registered doctor may lead to skin cancer.
Complications of eczema
Following consequences are seen in patients with eczema –
- Scarring
- Infection in the lesion
- Due to excessive itching, loss of sleep occurs
Sometimes people with severe atopic eczema have symptoms that can be easily detected, sometimes it is not easily noticeable at all.
Prevention of eczema flare-ups
Some preventive measures are helpful to reduce eczema flare-ups. There is no known cure for this.
- Using cotton-made cloth or blankets. Avoid any wool, stiff synthetic fabrics.
- Avoid exposure to dry weather, extreme temperatures, artificial perfume, bubble bath, harsh detergent, or soap.
- Try to use moisturizer soon after bathing.
- During dry weather uses a humidifier to keep up the moisture.
- If you have leg swelling, to prevent stasis dermatitis you must use compression stockings.
- During prolonged sitting raise your leg to increase blood flow.
- Avoid some sorts of plants, metals, jewelry, dish detergents, or any kind of cleaning solution to prevent any kind of contact dermatitis.
Negative Impacts on Psychology
Preschool children with atopic eczema may face bullying. It may cause negative impacts on their mental health. Developed countries have various organizations; which provide regional support groups to boost up their morals.
Children with atopic eczema need special care and proper counseling. Doing yoga, walking outside, taking medication, engaging in hobbies help them to gain self-confidence.
Prognosis
The prognosis of eczema depends on the type of eczema; as well as the treatment of it. It varies from person to person. Unfortunately, most children with atopic eczema face the same problem as adults. Contact dermatitis usually recovers within three weeks. But stasis dermatitis may last for years.